Please provide a detailed introduction to the classification of LCD screens

The classification of LCD screens is a multidimensional system, consisting of five core dimensions: core technology, interface type, display characteristics, appearance and size, and special functions.
Please provide a detailed introduction to the classification of LCD screens
The classification of LCD screens is a multidimensional system, and understanding their classification methods is crucial for product selection. Below, I will provide you with a clear and practical classification chart of LCD screens from five core dimensions: core technology, interface type, display characteristics, appearance and size, and special functions.
1. Classified by panel technology (core technology)
This is the fundamental determinant of basic display performance such as screen quality, viewing angle, and response speed.
TN: The advantages are low cost and extremely fast response speed (commonly used in early esports screens). The disadvantages are narrow viewing angle, poor color, and low contrast. The current situation is that it has gradually been phased out and is only applied in low-end or cost sensitive scenarios.
VA/MVA/PVA: The advantages are high contrast, pure black performance, and good viewing angle. The disadvantage is that the response speed is between TN and IPS, and there may be color shift. Commonly seen in mid to high end displays and televisions, the G150XVN01.1 you previously inquired about uses MVA technology.
IPS/PLS/ADS: Its advantages include excellent viewing angles and precise color reproduction, making it a mainstream high-end technology currently available. The disadvantage is that the cost is high and there is a problem of light leakage in the early stages. Widely used in high-end displays, mobile phones, tablets, and professional fields with strict color requirements.
2.Classified by interface type
The interface is the "language" that communicates between the screen and the main control board, determining compatibility and signal type.
LVDS: characterized by low voltage differential signals, strong anti-interference ability, and long transmission distance. It is the absolute mainstream interface for industrial screens, vehicle mounted screens, and large-sized screens. The models you previously focused on all use this interface.
EDP: characterized by embedded DisplayPort, high transmission rate, support for high resolution and high refresh rate. It is the mainstream interface for modern laptops and high-end tablets, gradually penetrating into the field of industrial control.
RGB/MCU: characterized by parallel interface, RGB interface performs better than MCU. Low cost, commonly found in small-sized screens (such as below 3.5 inches) and consumer electronics products.
MIPI: characterized by a mobile industry processor interface, ultra-high speed, and low power consumption. Specially designed for smartphones and mobile devices, it almost monopolizes this field.
3.Classified by display type and appearance
This is related to the integration and usage of the screen.
Display module: The most basic form, including LCD glass, driver IC, backlight, and PCB board, is the core of the screen. Secondary development integration is required. The "8-inch assembled screen" you mentioned belongs to this category.
Open Cell: Display panel without backlight. Manufacturers can customize backlighting themselves, which is flexible and commonly used in large-scale production such as televisions to reduce costs.
Touch screen integration:
External type: divided into "frame sticker" (with air layer, easy to reflect) and "full bonding" (filled with optical adhesive, more transparent display).
Embedded: such as In Cell (touch layer inside LCD panel) and On Cell (touch layer on panel), mainly used for high-end mobile phones, with ultra-thin structure.
Touch technology:
Resistance type: The advantage is low cost, it can be touched by any object (including wearing gloves, stylus), and is dustproof and waterproof. The disadvantage is that the light transmittance is low and it does not support multi touch. Suitable for special environments such as industrial control and medical equipment.
Capacitive: The advantage is high transparency, support for multi touch, and sensitive touch feel. The disadvantage is that it must be touched with a conductor (finger), which is costly. Widely used in consumer electronics and interactive terminals.
4.Classified by size and resolution
This is the most intuitive selection parameter, usually with a standard sequence.
Common sizes: from 0.96 inches to over 100 inches. Consumer electronics mainly include mobile phones (6-7 inches), tablets (8-13 inches), and monitors (24-34 inches). In the industrial field, there are richer aspect ratios and customized sizes.
Standard resolution: usually bound to size and aspect ratio, such as:
4: 3- Commonly seen in industry: 800x600 (SVGA), 1024x768 (XGA)
16: 9- Mainstream Consumption: 1920x1080 (FHD)
16: 10- Office/Professional: 1280x800 (WXGA), 1920x1200 (WUXGA)
Other ratios: such as 5:4, 21:9, etc.
5.Classified by special functions and characteristics
This is the key to meeting the specific application environment requirements and the value of industrial screens.
Wide temperature screen: capable of stable operation within a temperature range of -30 ℃ to+80 ℃ or even wider, suitable for use in vehicles, outdoors, and industrial sites.
High brightness screen: The backlight brightness can reach over 1000 nits, suitable for outdoor, medical diagnosis, aviation instruments and other strong light environments.
Anti peeping screen/wide-angle screen: Optical technology is used to limit the viewing angle to protect privacy or expand the viewing angle.
Sunlight readable screen: Combining high brightness, low reflection, and special optical processing to ensure clear visibility under sunlight.
Long life/high reliability backlight: using industrial grade LED, with a lifespan of up to 50000 to 100000 hours, ensuring long-term stable operation of the equipment.
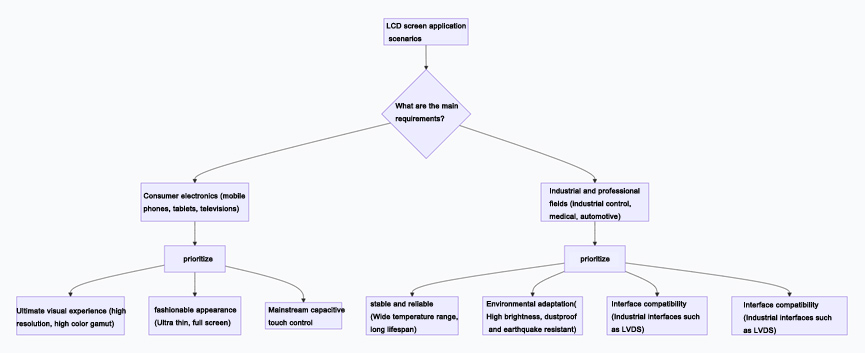
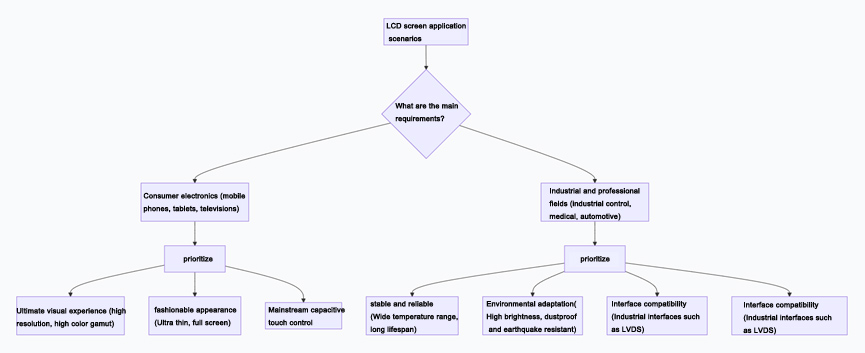
To help you better understand the core application scenarios of various screens, you can refer to the following decision path diagram:
Selection core suggestions
When selecting an LCD screen for a project, it is recommended to follow the following steps:
Setting the environment: Firstly, clarify the usage environment of the equipment (indoor, outdoor, temperature and humidity, electromagnetic interference), which will directly determine whether special functions such as wide temperature, high brightness, and reinforcement are needed.
Fixed interaction: Determine the human-computer interaction method (whether to touch, use fingers or gloves/stylus), which determines whether to choose a capacitive screen or a resistive screen.
Size and Resolution: Determine the physical size and resolution based on the device's structural space and the amount of information to be displayed.
Fixed interface: Select the matching screen interface (such as LVDS or eDP) based on the output interface of the main control board (such as the interface supported by GPU or main control chip).
Determine technology and budget: Within the budget range, choose the appropriate panel technology (IPS/VA, etc.) based on the requirements for image quality (color, viewing angle, contrast).
I hope this detailed classification guide can help you make more systematic selections and decisions in your work. If you can provide specific application scenarios (such as medical equipment, outdoor handheld terminals, etc.), I can provide you with more targeted selection analysis.
AUO LCD DISPLAY:https://www.idtdisplay.com/products/AUO_LCD_Displays