What is the difference between LCD modules and liquid crystal display?

The LCD module is the core display component of the "semi-finished product ", while the LCD display is the complete device of the "finished product "
The LCD module is the core display component of the "semi-finished product", while the LCD display is the complete device of the "finished product".
Below is a detailed breakdown:
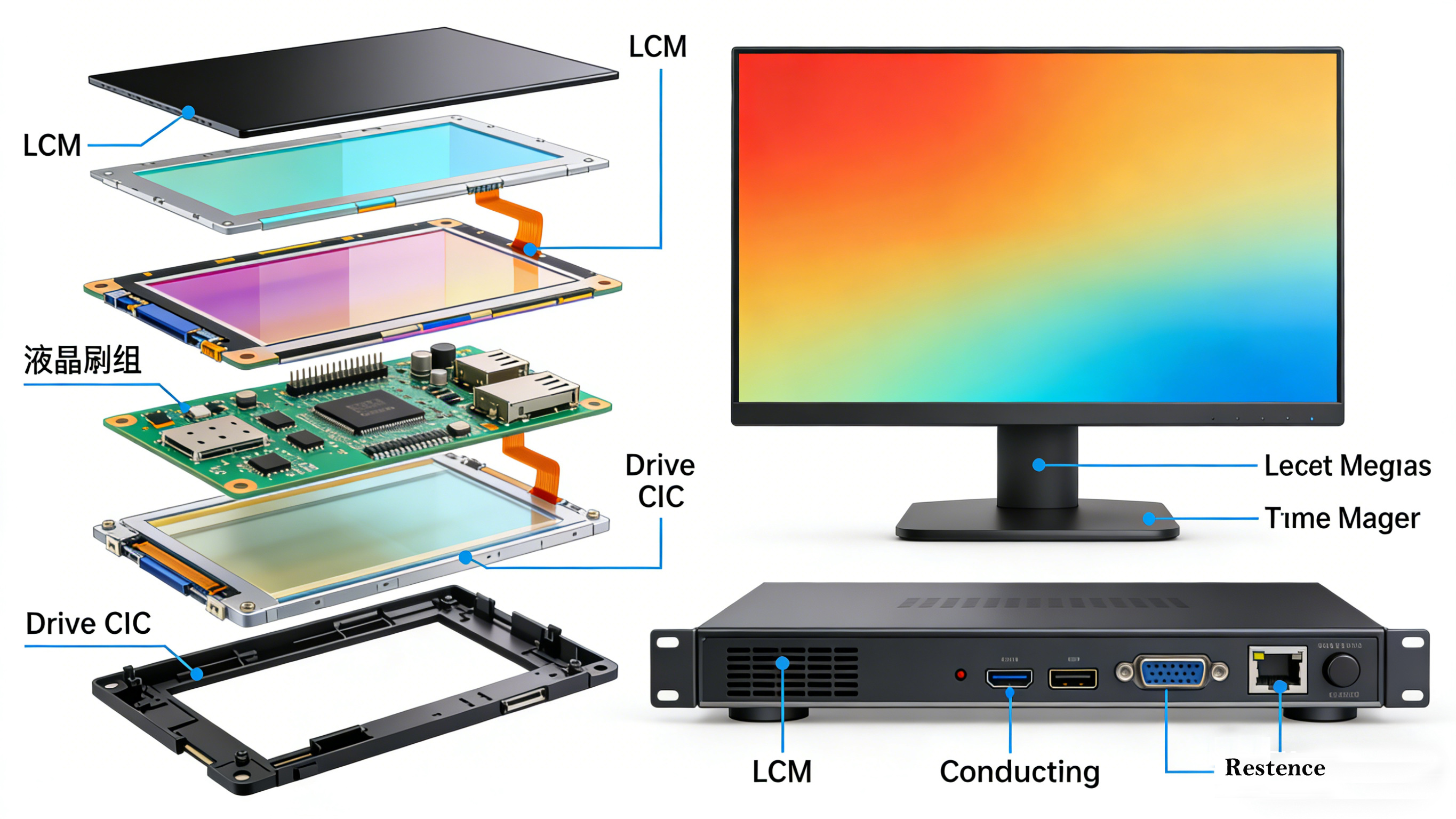
LCD module
You can understand it as the "heart" or "engine" of a monitor. It is a component that integrates a liquid crystal panel and necessary driver circuits together, but does not include peripheral components such as the housing, power supply, signal interface board, control buttons, etc. required for the final product.
Core components:
1. Liquid crystal glass (Panel): The most essential part, including liquid crystal materials, color filters, TFT transistors, etc., directly responsible for imaging.
2. Backlight unit: provides a light source for LCD glass, usually including LED light strips, light guide plates, diffusion films, prism sheets, etc.
3. Drive circuit: including:
Source driver chip&gate driver chip: directly connected to the wiring of the liquid crystal glass, responsible for precise control of the switch of each pixel point.
Timing controller: receives external signals and commands the source and gate driver chips to operate.
Power management circuit: provides the required voltage for backlight and driver chips.
Key Features:
Industrial grade components: mainly aimed at manufacturers, engineers, DIY enthusiasts, or the repair market.
Secondary development required: After purchase, users or manufacturers need to design the casing, configure the power supply, install the signal processing board (such as HDMI/VGA interface board), and write or configure driver software in order to become a usable display device.
Original interface: Typically, pure display signals and power inputs are provided through board to board connectors such as LVDS, eDP, MIPI, rather than common consumer interfaces such as HDMI and DP.
Common applications: industrial equipment (such as medical instruments, industrial control screens), self-service terminals (ATMs, ticket machines), embedded systems, portable devices, and production lines of display/television manufacturers.
liquid crystal display
This is the "monitor" we see on the desktop in our daily lives, or the "TV" we buy in the mall. It is a complete, plug and play consumer electronics product.
Core components: It includes a liquid crystal module and adds:
1. Shell (front frame, rear shell, bracket): Provides structural support, protection, and aesthetics.
2. Signal processing motherboard (main control board): This is the key difference. This board integrates various video input interfaces such as HDMI, DP, VGA, USB, as well as chips responsible for image processing, color management, and OSD menu control (such as MediaTek and Realtek's solutions).
3. Power board: Convert the mains power (220V) into the DC power required by the module and motherboard. It may be internal or external.
4. Control buttons/joysticks: used to operate OSD menus.
5. Speaker (optional): Integrated audio output function.
6. Factory pre installed drivers and firmware: guaranteed to be ready to use out of the box.
Key Features:
Consumer grade products: aimed at end-users.
Plug and play: Users only need to connect the power cable and video cable (such as HDMI) to use it.
Fully functional: It has a complete input interface, image adjustment (brightness, contrast, color temperature), audio output and other functions.
Summary of main differences
Feature | liquid crystal display | |
Nature | Industrial components/semi-finished products | Consumer electronics products/finished products |
Constitute | LCD panel+backlight+basic driving circuit | LCD module+shell+signal motherboard+power supply+interface+buttons, etc |
Interface | Industrial interfaces such as RGB, LVDS, eDP, MIPI, etc | HDMI, DP, VGA, USB and other universal video interfaces |
Usage | Need for secondary development, integration, and configuration of drivers | Plug and Play |
Target audience | Manufacturers, engineers, and maintenance personnel | Ordinary consumers and enterprise users |
Scalability | High, can customize peripheral circuits according to needs | Low, the function has been fixed |
For example | The "laptop screen assembly" and "TV LCD panel" you bought online | The Dell, Samsung, LG brand monitors you bought online |
A vivid metaphor
The LCD module is like the core powertrain of a car's engine, gearbox, and chassis. It has the most essential functions of a car, but cannot be driven directly on the road.
LCD displays are like a whole car. On the basis of the core powertrain, it has added steering wheel, seats, body shell, headlights, center console entertainment system, etc., becoming a complete product that can be driven directly.
Significance in practice
Repair: If your monitor is broken, it could be a module issue (such as lines or black spots on the screen), or it could be a motherboard or power issue. The maintenance personnel will determine whether to replace the entire module (high cost) or only replace the peripheral board (low cost).
Procurement: If you are developing a smart home terminal, you will purchase LCD modules and integrate them into your product design. If you are purchasing computer peripherals for the office, you can directly buy LCD monitors.
Cost: LCD modules of the same size and parameters are usually priced much lower than finished displays of the same specifications, as they do not include brand added value, peripheral components, R&D amortization, and channel profits.
I hope this explanation can help you clearly distinguish between these two concepts!
TFT LCD:https://www.idtdisplay.com/