Detailed Introduction - Development History of TFT LCD

The development of TFT LCD has moved from the laboratory to the global industry, driven by material innovation, process improvement, and application expansion Despite facing challenges from new technologies such as OLED
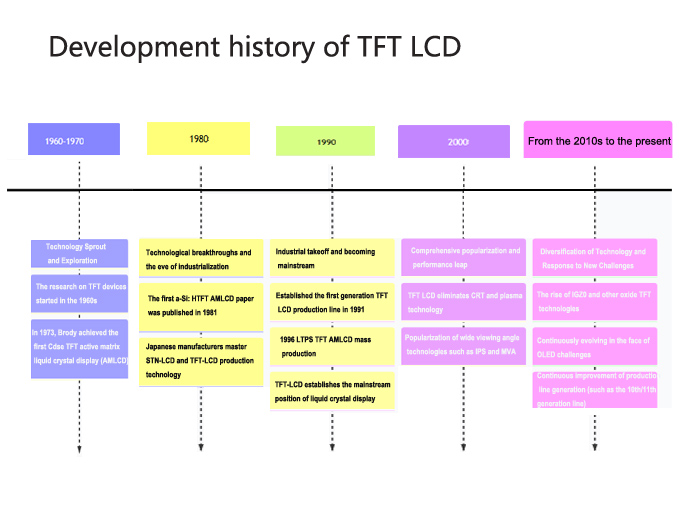
The development process of TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display) is a commercial and technological miracle that has gone from a laboratory concept to ubiquitous presence. The following timeline can help you quickly understand the key milestones in its development:
Next, let's take a detailed look at the story of each stage.
Technology Sprout and Exploration (1960-1970s)
At this stage, TFT LCD technology has achieved a breakthrough from concept to physical implementation.
Technical starting point: The research on TFT devices began in the early 1960s. Paul K. Weimer from RCA developed TFT technology using John Wallmark's patent.
First combination: In 1968, Bernard Lechner from RCA implemented TFT technology for the first time in liquid crystal displays.
The first prototype: In 1973, the T. P. Brody team successfully implemented the first active matrix liquid crystal display (AMLCD) using cadmium selenide (CdSe) TFT, demonstrating the feasibility of driving each pixel with TFT.
Early application: At that time, LCD was mainly a twisted nematic (TN) technology for monochrome display, applied to calculators, electronic watches, etc. These early LCDs had high power consumption, low contrast, and were expensive.
Technological breakthroughs and the eve of industrialization (1980s)
The breakthrough in materials and processes has cleared the obstacles for the large-scale production of TFT LCDs.
Key material breakthrough: Spear and LeCooper from Dundee University in the mid-1970s reduced the defect state density of amorphous silicon thin films by doping hydrogen, solving the problem of difficulty in forming conductive channels through gate voltage control in TFT preparation.
The arrival of a-Si: H TFT: In 1981, the first AMLCD paper based on hydrogen doped amorphous silicon TFT was published. Amorphous silicon TFT has paved the way for the large-scale application of TFT LCD due to its advantages of low manufacturing cost and good performance consistency.
Japan's leading role: By the late 1980s, Japanese manufacturers had mastered the production technology of STN-LCD and TFT-LCD, and the LCD industry began to enter a period of rapid development.
Industrial takeoff and becoming mainstream (1990s)
In the 1990s, TFT LCD began large-scale industrialization and quickly replaced other display technologies.
The development of the generation line: In 1991, the first generation TFT LCD production line (300mm x 350mm) was established, marking the entry of TFT LCD into the era of large-scale industrialization. The continuous expansion of glass motherboard size drives the increase of panel size and cost reduction.
Performance improvement and technological diversification:
The display of TFT LCD adopts a "back transparent" illumination method and is equipped with a semiconductor switch device for each pixel, making each node relatively independent and continuously controllable, improving response speed and accurately controlling display grayscale, resulting in more realistic colors.
In 1996, AMLCD based on low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) TFT achieved mass production. LTPS TFT has advantages such as high mobility and good stability, making it suitable for small-sized high-end displays.
Application Expansion: TFT LCD began to be mainly used in laptop manufacturing and gradually established its mainstream position in LCD displays.
Comprehensive Popularization and Performance Leap (2000s)
During this period, TFT LCD achieved comprehensive dominance in both large and small screen sizes and continued to undergo technological optimization.
Eliminating old technologies: TFT LCD display technology has dominated the display market by 2020, and in the past 20 years, it has eliminated CRT and plasma technologies.
Improved performance: By adopting new TFT LCD screen technologies such as IPS (in-plane switch) and MVA (multi area vertical arrangement), the early issues of viewing angle and response time have been effectively resolved. TFT LCD, based on its advantages of lightness and thinness, ensures its dominance in the display market with perfect graphics and fast response characteristics.
Applications are everywhere: TFT LCD has been widely used in various aspects of life, from small-sized mobile phones, cameras, digital cameras, medium-sized laptops, desktops, to large-sized home televisions and large projection devices.
Technological diversification and response to new challenges (2010s present)
Faced with the challenges of new display technologies, TFT LCD technology is still constantly innovating and developing towards more diverse directions.
The rise of oxide TFTs: amorphous oxide semiconductor TFTs represented by indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) have emerged. IGZO TFT can achieve high mobility at lower process temperatures and has the advantages of steep subthreshold swing and low leakage current, which is conducive to achieving large-area performance consistency. It is suitable for flexible large-sized AMOLED displays and low-power displays.
Dealing with OLED challenges: The only challenge currently dominated by the TFT LCD market comes from OLED (organic light-emitting diodes) and Micro LED (which may still be in the laboratory stage). TFT LCD actively responds to competition by developing technologies such as Mini LED backlighting to enhance contrast and image quality.
Continuous technological progress: TFT LCD technology is still advancing, such as towards larger sizes (such as the 19 inch model showcased by Samsung at CES), high resolution (such as 8K), high refresh rate (suitable for gaming), wide viewing angle (up to 170 degrees), high contrast (meeting demanding requirements for aviation computer displays, medical displays, etc.), and combined with PCAP (capacitive touch screen). The generation of production lines continues to improve (such as the 10th/11th generation lines), further reducing costs and improving efficiency.
summary
Looking back at the development of TFT LCD, it has moved from the laboratory to the global industry, driven by material innovation, process improvement, and application expansion. Despite facing challenges from new technologies such as OLED, TFT LCD still maintains strong vitality in many fields through low cost, high performance, and continuous technological innovation (such as Mini LED backlight). In the future, TFT LCD technology is expected to continue developing towards ultra large size, ultra-high resolution, low power consumption, and integration with flexibility and new forms.
I hope the above summary can help you gain a deeper understanding of the magnificent development history of TFT LCD. If you are particularly interested in a specific technology or a comparison of different TFT technologies, I would be happy to provide further introduction.
AUO LCD DISPLAY:https://www.idtdisplay.com/products/AUO_LCD_Displays/