The difference between dark spots and bright spots on LCD screens

Professional analysis of dark spots and bright spots on LCD screens, including differences and comparisons, causes and effects, applicable to product documentation and technical popularization
Professional analysis of dark spots and bright spots on LCD screens, including differences and comparisons, causes and effects, applicable to product documentation and technical popularization:
The core difference between dark spots and bright spots on LCD screens
Characteristic | Dead Pixel | Stuck Pixel/Bright Dot |
Display Status | Permanently non luminous, black in color | Permanently bright, presenting a fixed color of white/red/green/blue |
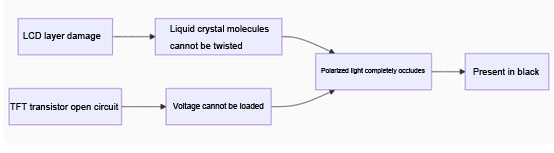
Cause | Physical damage to LCD unit or failure of TFT transistor | LCD unit stuck or signal circuit malfunction |
Visible Scene | Obvious on a light background (such as a white screen) | Obvious under dark background (such as black screen) |
Visual impact | Similar to the image 'missing' | Similar to visual "pollution" (especially when watching movies in dark environments) |
Repairability | Irreparable (physical damage) | A few can be temporarily restored through pixel repair software |
Deep analysis of technical principles
Mechanism of dark spot formation
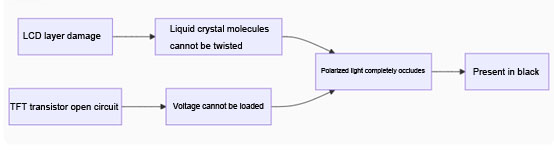
Mechanism of Highlight Formation

Special effects in industrial scenarios
Medical display equipment
Dark spot: may be misdiagnosed as tissue shadow (such as X-ray observation)
Highlight: Easy to be misjudged as calcification or bleeding points
▶ Industry standard requirement: 0 bad pixels (Class 1 level)
Industrial control screen
Dark spot: causing missing key data in the monitoring screen
Highlight: Interference alarm status recognition (such as misjudging the red alarm light)
▶ Allow ≤ 3 bad pixels (Class 2 level)
Car display screen
Nighttime highlights: Diverting the driver's attention (similar to direct high beam)
Dark spot: Risk of loss of navigation key intersection information
User authentication method (three-step self check)
1. Complete solid color testing method
Black Screen → Observe Highlights
Full white screen → Observe dark spots
Three primary color testing → Identify color highlights
2. Magnifying mirror assistance
Highlight: Fixed position illumination (non screen dust)
Dark spot: No sub-pixel emission (different from small foreign object occlusion) 3
Professional tool validation
Automatically scan using software such as Dead Pixel Test
Industrial grade testing: Microscopic camera+image analysis system
Industry Quality Standard (ISO 13406-2 Specification)
Bad dot type | Class 1(Medical) | Class 2(Industrial grade) | Class 3(Consumer Grade) |
Dark spot | 0 | ≤2 | ≤5 |
Highlights | 0 | ≤2 | ≤5 |
Three color highlights | 0 | ≤1 | ≤3 |
Total number of bad pixels | 0 | ≤3 | ≤8 |
Purchase suggestions
1. Industrial/Medical Equipment
Request the supplier to provide a distribution map of bad pixels and a Class certificate
The contract states: "Upon arrival inspection, bright/dark spots exceeding the standard were found, and the entire batch was returned“
2. Consumer grade products
National standards allow for the presence of bad pixels (such as laptop screens with ≤ 3)
Priority should be given to brands that provide "zero bad point guarantee" (with a premium of 10-15%)
3. Basis for Rights Protection
O Keep unboxing inspection videos
According to Article 7 of the "Three Guarantees Regulations for Monitors": "If there are more than 3 bad pixels during startup, they can be returned or exchanged“
Technology trend: Micro LED technology will completely eliminate the problem of bad pixels (single pixel independent packaging), and current LCD screens still need to pay attention to the manufacturer's warranty terms